Did you know that some traders believe implied volatility is like the weather—sometimes sunny, sometimes stormy, and always unpredictable? In the world of day trading options, understanding implied volatility is crucial for making informed decisions. This article dives deep into the fundamentals of implied volatility, explaining its role in option pricing, its significance for day traders, and how it impacts risk management. You’ll learn how to measure it, identify trading opportunities, and the difference between stocks and ETFs. We also cover strategies for high implied volatility, the influence of market events, and the potential pitfalls of relying solely on this metric. With insights from DayTradingBusiness, you’ll be equipped to adjust your trading strategy effectively and navigate the complexities of implied volatility in day trading.
What is implied volatility in options trading?
Implied volatility in options trading reflects the market's expectations for future price fluctuations of the underlying asset. It indicates how much the market thinks the asset's price will move, impacting option premiums. High implied volatility suggests greater expected movement, leading to higher option prices, while low implied volatility indicates less movement and lower prices. Day traders often use implied volatility to gauge market sentiment and identify potential trading opportunities.
How does implied volatility affect option pricing?
Implied volatility directly impacts option pricing by reflecting market expectations of future price movements. Higher implied volatility increases option premiums, making options more expensive due to the anticipated larger price swings. Conversely, lower implied volatility decreases premiums, as the market expects less movement. Day traders often monitor implied volatility to gauge potential price action and adjust their strategies accordingly. Understanding these dynamics helps traders make informed decisions about when to buy or sell options.
Why is implied volatility important for day traders?
Implied volatility is crucial for day traders because it indicates market expectations for future price fluctuations. Higher implied volatility suggests greater potential for price swings, which can lead to profitable trading opportunities. It helps traders assess option pricing and identify when options may be overvalued or undervalued. Understanding implied volatility allows day traders to time their entries and exits more effectively, maximizing their gains while managing risk.
How can I measure implied volatility for options?
To measure implied volatility for options, use the Black-Scholes model or other pricing models that factor in the underlying asset's current price, strike price, time to expiration, risk-free interest rate, and dividends. You can also check market data from options exchanges or financial platforms that provide implied volatility calculations. Look for the "implied volatility" metric on your trading platform, as it reflects market expectations of future volatility based on current option prices.
What are the common indicators of implied volatility?
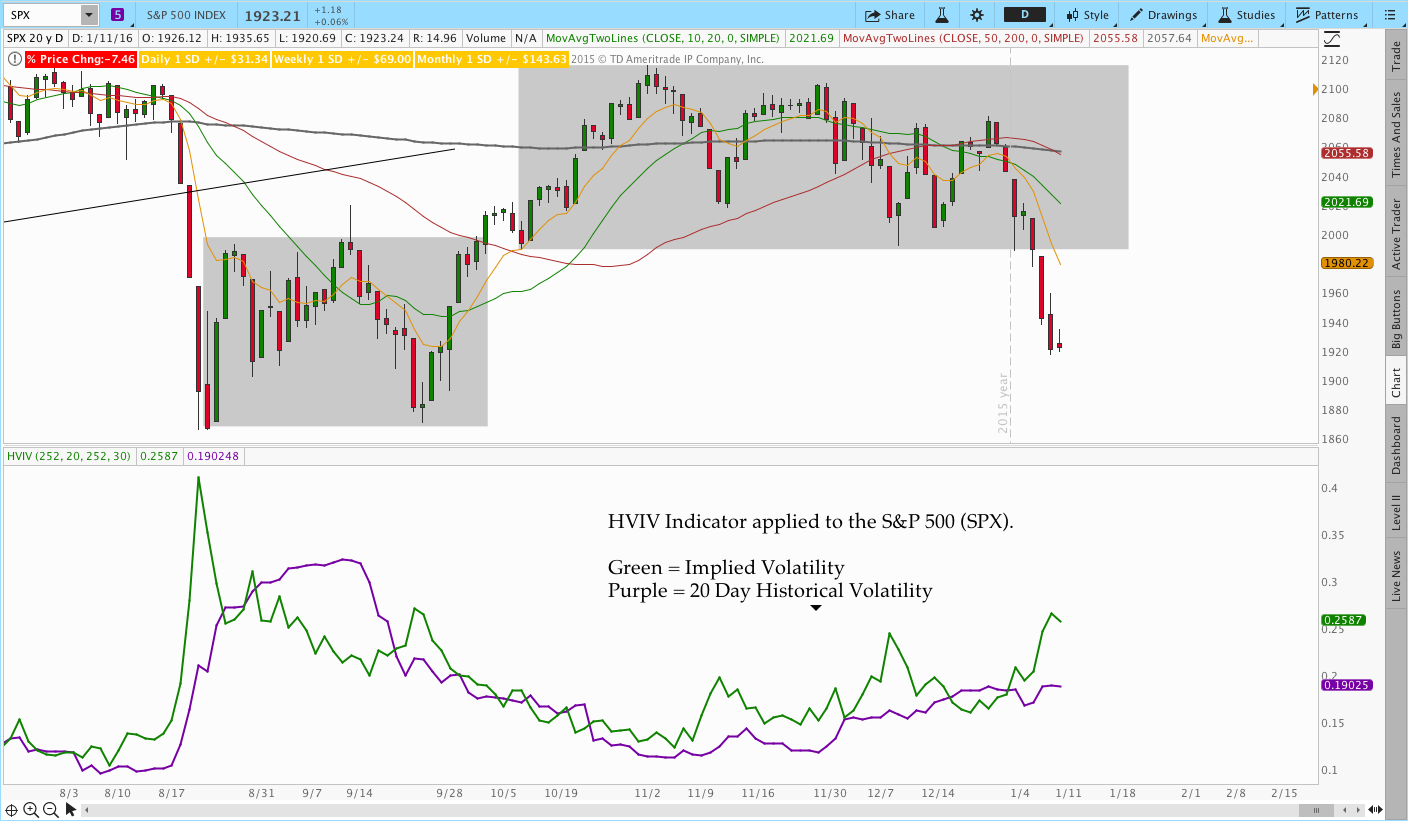
Common indicators of implied volatility include the VIX index, historical volatility comparisons, options pricing models like the Black-Scholes model, volume and open interest in options contracts, and changes in the bid-ask spread. Traders often look for spikes in implied volatility before earnings reports or major news events, as these can signal potential price movements.
How does implied volatility impact risk management in day trading?
Implied volatility (IV) directly impacts risk management in day trading by influencing options pricing and potential price movement. High IV suggests greater expected price swings, increasing the risk of large losses or gains. Traders use IV to assess the likelihood of hitting profit targets and to set stop-loss orders effectively. When IV is high, options premiums increase, which can lead to higher costs for entering trades. Conversely, low IV can indicate lower risk but may also limit profit potential. Understanding IV helps traders determine optimal entry and exit points, adjust position sizes, and implement strategies that align with market volatility.
Can I predict future implied volatility movements?
Yes, you can attempt to predict future implied volatility movements by analyzing historical volatility patterns, market sentiment, and specific events like earnings reports or economic announcements. Tools like options pricing models and volatility indicators can help gauge expected shifts. However, predictions are inherently uncertain and should be approached with caution.
How does implied volatility differ between stocks and ETFs?
Implied volatility (IV) for stocks often reflects the market's expectation of price movement based on company-specific news, earnings reports, or events. In contrast, IV for ETFs generally accounts for broader market trends and sector performance. Stocks can show more significant spikes in IV due to their sensitivity to unique catalysts, while ETFs tend to have more stable IV levels since they represent a basket of stocks. This difference can affect your day trading strategies, as higher IV in stocks might present more trading opportunities, but also greater risk.
What strategies can I use with high implied volatility?
Use the following strategies with high implied volatility in day trading options:
1. Sell Options: Write covered calls or cash-secured puts to capitalize on high premiums.
2. Iron Condors: Set up an iron condor to profit from range-bound price action while benefiting from time decay.
3. Straddles and Strangles: Buy straddles or strangles to take advantage of significant price movements, especially around earnings reports.
4. Volatility Skew: Look for discrepancies in implied volatility across different strikes to identify potential mispricings.
5. Hedge Positions: Use options to hedge other positions in your portfolio, protecting against adverse price movements.
Each strategy leverages the unique characteristics of high implied volatility for potential profit.
How do market events influence implied volatility?
Market events, like earnings reports or economic data releases, can significantly influence implied volatility. When such events are anticipated, traders expect larger price swings, driving up implied volatility as options become more expensive. Conversely, once the event occurs, implied volatility often drops as uncertainty decreases. This fluctuation can create opportunities for day traders, who can capitalize on the changing premiums of options before and after these events.
What are the pitfalls of relying on implied volatility?
Relying on implied volatility (IV) in day trading options can lead to several pitfalls. First, IV can be misleading; high IV doesn't always guarantee price movement. Traders may overestimate potential profits, resulting in poor decision-making. Additionally, IV often reflects market sentiment rather than actual price action, leading to miscalculations. It can change rapidly, impacting option pricing unpredictably. Lastly, focusing solely on IV might divert attention from other critical factors like underlying asset performance or market trends, increasing risk.
How can I use implied volatility to identify trading opportunities?
To use implied volatility (IV) for trading opportunities, first monitor the IV levels of options. High IV suggests options are relatively expensive, indicating potential overvaluation. Look for opportunities to sell options when IV is high, especially if you believe the underlying asset won't move significantly. Conversely, low IV indicates undervalued options, making it a good time to buy if you anticipate larger price swings.
Use IV changes as signals. If IV rises sharply before earnings, consider straddles or strangles for potential profit from big moves. When IV drops after an event, consider selling options to capitalize on the decrease. Always pair IV analysis with technical indicators for better precision in your trades.
What role does implied volatility play in option spreads?
Implied volatility (IV) is crucial in option spreads as it directly affects option pricing. Higher IV typically increases option premiums, making spreads more expensive. Traders use IV to gauge market sentiment; if IV is rising, it suggests increased uncertainty, which can impact spread profitability. In certain strategies, like credit spreads, low IV can be advantageous since options are cheaper, enhancing potential returns. Understanding IV helps traders make informed decisions about entry and exit points, maximizing their day trading profits.
How does historical volatility compare to implied volatility?
Historical volatility measures past price fluctuations of an asset over a specific period, while implied volatility reflects the market's expectations of future volatility based on option prices. Historical volatility uses actual price data, whereas implied volatility is derived from the options market and indicates trader sentiment. In day trading options, implied volatility can signal potential price movement and is crucial for assessing option premiums. Higher implied volatility often leads to higher premiums, making it essential for traders to understand both types to make informed decisions.
How Does Implied Volatility Affect Day Trading Options?
Implied volatility in day trading options indicates the market's expectations of future volatility. Higher implied volatility generally leads to higher option premiums, making options more expensive. Traders use implied volatility to assess potential price movements and to identify optimal entry and exit points. Understanding this can significantly impact day trading strategies.
Learn more about: Understanding Options in Day Trading
What resources are available for tracking implied volatility?
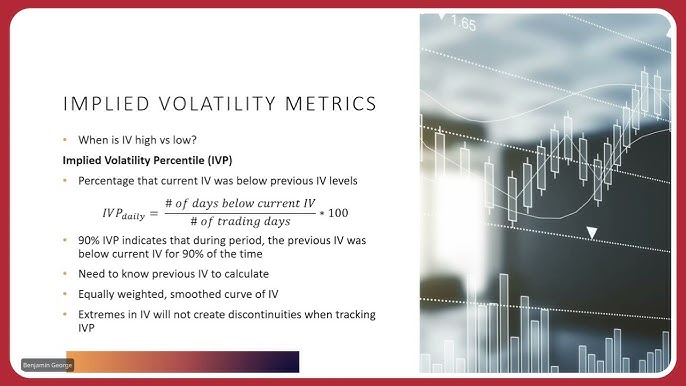
To track implied volatility, use resources like the CBOE (Chicago Board Options Exchange) for real-time data, and platforms like Thinkorswim or Interactive Brokers that offer built-in tools. Websites like Market Chameleon and Optionistics provide detailed charts and analytics. For a more hands-on approach, consider financial news services like Bloomberg or Reuters, which offer market insights and volatility indices. Additionally, options analysis software like Option Samurai can help you gauge implied volatility effectively.
How should I adjust my trading strategy based on changes in implied volatility?
Adjust your trading strategy based on changes in implied volatility by first assessing the current volatility environment. If implied volatility rises, consider selling options to take advantage of higher premiums. Conversely, if it falls, buying options may be more beneficial, as premiums tend to decrease.
Look for opportunities to enter trades when implied volatility is low and expected to rise, as this can lead to profitable moves. Additionally, use straddles or strangles in high volatility situations to capitalize on potential price swings. Always monitor your positions and adjust stop-loss orders accordingly to manage risk effectively.
Conclusion about The Role of Implied Volatility in Day Trading Options
Understanding implied volatility is essential for successful day trading options. It directly influences option pricing, risk management, and trading strategies. By measuring and analyzing implied volatility, traders can identify opportunities and make informed decisions, particularly around market events. While it holds significant potential, caution is necessary to avoid common pitfalls. Leveraging the insights provided by DayTradingBusiness can enhance your trading approach and lead to more effective strategies in navigating the complexities of implied volatility.
Learn about Frequently Asked Questions About Day Trading Options