Did you know that the average day trader spends about six hours a day staring at charts, which is more than the time it takes to binge-watch an entire season of a hit TV show? In the ever-evolving world of day trading, understanding essential terminology is crucial for success. This article delves into the fundamentals of day trading, explaining key concepts such as candlestick patterns, stop-loss orders, and the impact of leverage. We will clarify the difference between market and limit orders, explore scalping strategies, and highlight the significance of support and resistance levels. Additionally, we’ll cover how news events can trigger volatility and the importance of managing risk. For anyone looking to navigate the fast-paced trading environment, this guide from DayTradingBusiness is your go-to resource for mastering the essential day trading terminology.
What is day trading and how does it work?
Day trading involves buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day to capitalize on short-term price movements. Traders aim to make quick profits by executing multiple trades, often using leverage. Key terms include:
1. Scalping: Making numerous small trades to profit from minor price changes.
2. Swing Trading: Holding positions for several days to capture larger price swings.
3. Pips: The smallest price movement in currency pairs, crucial for forex trading.
4. Margin: Borrowed funds used to increase potential returns but also risk.
5. Stop Loss: An order to sell a security when it reaches a certain price to limit losses.
6. Limit Order: An order to buy or sell at a specific price or better.
Understanding these terms is vital for effective day trading strategies.
What are the key terms every day trader should know?
1. Bid and Ask: The price buyers are willing to pay (bid) and the price sellers want (ask).
2. Spread: The difference between the bid and ask prices.
3. Volume: The number of shares traded during a specific period.
4. Liquidity: How easily an asset can be bought or sold without affecting its price.
5. Market Order: An order to buy or sell immediately at the current market price.
6. Limit Order: An order to buy or sell at a specified price or better.
7. Stop-Loss Order: An order to sell a security when it reaches a certain price to limit losses.
8. Margin: Borrowed funds from a broker to trade larger positions than your account balance.
9. Technical Analysis: Analyzing price charts and indicators to make trading decisions.
10. Pattern Day Trader (PDT): A trader who executes four or more day trades within five business days.
How do candlestick patterns influence day trading?
Candlestick patterns help day traders identify potential market reversals or continuations. Patterns like doji, hammer, and engulfing indicate buying or selling pressure. Traders use these signals to make quick decisions on entry and exit points, aiming for maximum profit within short timeframes. Understanding these patterns enhances trading strategies and improves market timing.
What is a stop-loss order in day trading?
A stop-loss order in day trading is an instruction to sell a stock once it reaches a specified price, limiting potential losses. For example, if you buy a stock at $50 and set a stop-loss at $48, the stock will automatically sell if it drops to that price. This strategy helps manage risk and protect your capital in volatile markets.
How does leverage affect day trading profits and risks?
Leverage amplifies both profits and risks in day trading. When you use leverage, you can control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital, potentially increasing your gains if the trade goes in your favor. For example, with 10x leverage, a 1% increase in the asset price can yield a 10% profit on your investment.
However, leverage also magnifies losses. A 1% decrease in the asset price can lead to a 10% loss, quickly eroding your capital. This risk means that while leverage can enhance profits, it also increases the likelihood of significant losses, making risk management crucial for day traders.
What is the difference between a market order and a limit order?
A market order is an instruction to buy or sell a stock immediately at the current market price. A limit order, on the other hand, sets a specific price at which you want to buy or sell; it only executes if the market reaches that price. In short, market orders prioritize speed, while limit orders prioritize price.
What does “scalping” mean in day trading?
In day trading, "scalping" refers to a strategy where traders make numerous quick trades throughout the day to profit from small price movements. Scalpers aim to buy and sell stocks rapidly, often holding positions for just a few seconds to a few minutes, capitalizing on minor fluctuations. This method requires a keen sense of timing and a strong focus on market trends.
What are technical indicators used in day trading?
Technical indicators used in day trading include moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), Bollinger bands, MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence), and volume indicators. Moving averages help identify trends, while RSI indicates overbought or oversold conditions. Bollinger bands show price volatility, MACD signals potential buy or sell opportunities, and volume indicators assess the strength of a price movement. These tools aid traders in making informed decisions based on market data.
How do support and resistance levels impact trading decisions?
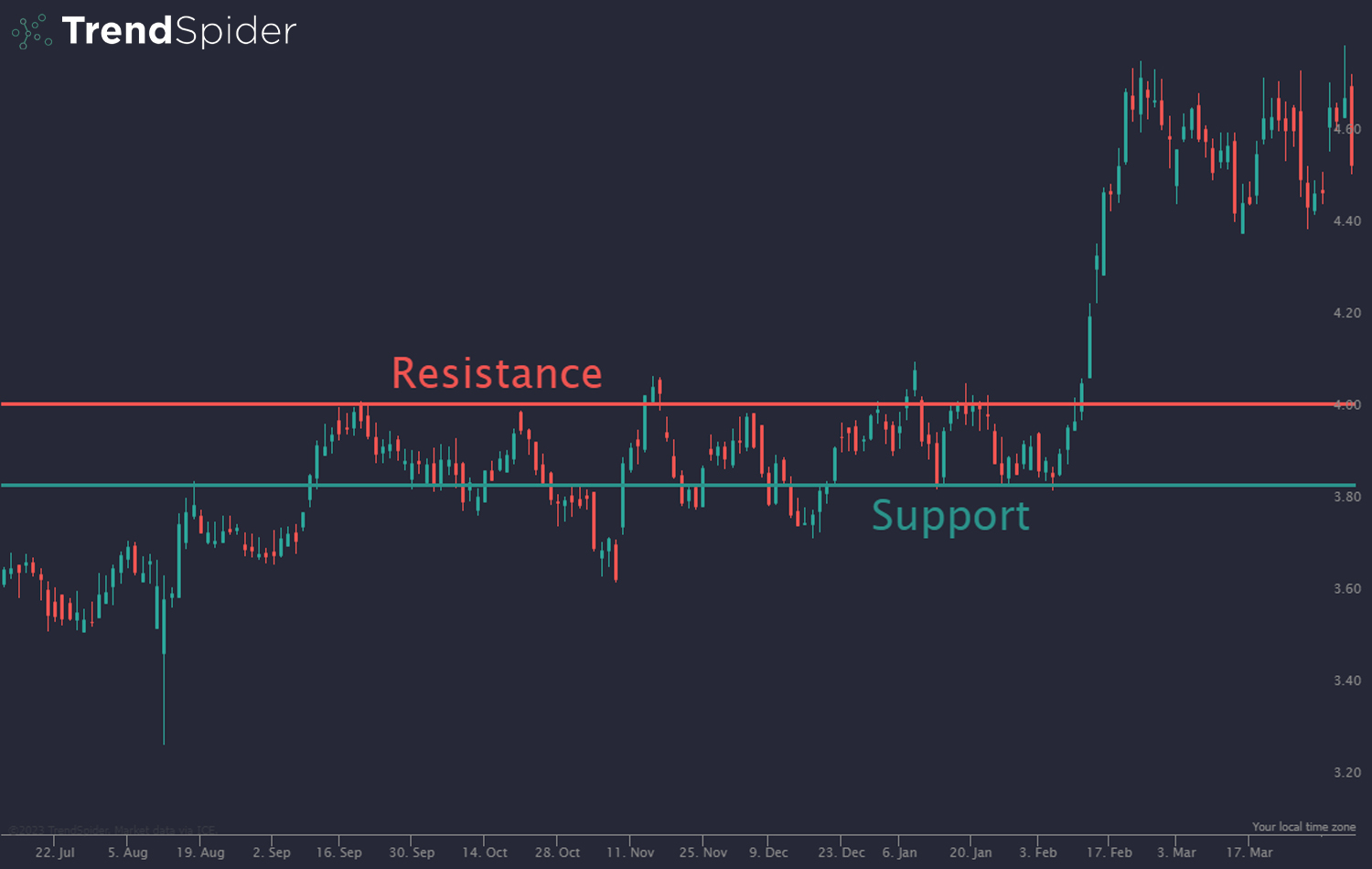
Support and resistance levels guide traders in making decisions about entry and exit points. Support acts as a price floor where buying interest increases, while resistance serves as a ceiling where selling pressure mounts. Traders often buy near support and sell near resistance to capitalize on price reversals. Recognizing these levels helps manage risk and set stop-loss orders effectively. When prices break through support or resistance, it can signal a trend continuation, influencing traders to adjust their strategies accordingly.
What is the significance of volume in day trading?
Volume in day trading refers to the number of shares or contracts traded in a specific period. It indicates market activity and liquidity. High volume often signals strong interest in a stock, making it easier to enter or exit positions without significant price changes. Traders use volume to confirm trends; for example, an upward price movement with high volume suggests strength, while low volume may indicate a lack of conviction. Understanding volume helps traders identify potential reversals and validate breakout patterns, making it a crucial aspect of effective day trading strategies.
What are trading strategies commonly used by day traders?
Common trading strategies used by day traders include:
1. Scalping: Making quick trades to profit from small price movements.
2. Momentum Trading: Buying stocks showing strong upward or downward trends.
3. Breakout Trading: Entering a position when the price breaks through resistance or support levels.
4. Reversal Trading: Identifying potential trend reversals and trading against the prevailing trend.
5. Range Trading: Buying at support levels and selling at resistance levels within a defined range.
These strategies rely on technical analysis, charts, and indicators to make quick and informed decisions.
## What Are the Key Terms and Concepts in Day Trading?
Day trading is the practice of buying and selling financial instruments within the same trading day, aiming to capitalize on short-term price movements.
Learn more about: What is Day Trading?
How do news events affect day trading volatility?
News events significantly impact day trading volatility by causing rapid price fluctuations. For example, earnings reports, economic data releases, or geopolitical developments can lead to sharp movements in stock prices. Traders often capitalize on this volatility by executing quick trades based on news reactions. High volatility can increase the potential for profit but also raises risks, making it crucial for day traders to stay informed and react swiftly.
Learn about How to Stay Updated on Crypto Market News for Day Trading
What is slippage and how does it affect day trading?

Slippage is the difference between the expected price of a trade and the actual price at which the trade is executed. In day trading, slippage can occur during fast market movements or low liquidity. This impacts profits by increasing costs on entry or exit points, potentially leading to losses or reduced gains. Traders must account for slippage in their strategies to ensure accurate risk management and execution.
What does it mean to go long or short in day trading?
Going long in day trading means buying a stock or asset with the expectation that its price will rise, allowing you to sell it later for a profit. Going short involves selling a stock you don’t own, betting that its price will drop, so you can buy it back at a lower price and profit from the difference.
How can traders manage risk effectively in day trading?
Traders can manage risk effectively in day trading by using several key strategies. First, set a strict stop-loss order for each trade to limit potential losses. Second, determine position size based on your account balance and risk tolerance; typically, risk no more than 1-2% of your capital on a single trade. Third, diversify your trades to avoid overexposure to one asset. Fourth, use trailing stops to lock in profits while allowing for potential upside. Lastly, continuously review and adjust your trading plan based on performance and market conditions.
What are the tax implications of day trading?
Day trading can lead to significant tax implications. Profits are typically considered short-term capital gains, taxed at ordinary income rates. If you qualify as a "trader" under IRS rules, you might benefit from the mark-to-market accounting method, allowing you to deduct losses more effectively. Keep track of all trades for accurate reporting, as the IRS requires detailed records. Additionally, be aware of the wash sale rule, which can affect your ability to claim losses.
Conclusion about Essential Day Trading Terminology You Need to Know
Understanding essential day trading terminology is crucial for success in the fast-paced trading environment. Familiarity with key concepts like candlestick patterns, stop-loss orders, and market versus limit orders can significantly enhance trading strategies. Moreover, grasping the impact of leverage, support and resistance levels, and trading volume will help in making informed decisions. By mastering these terms, traders can navigate market volatility and manage risks effectively. For comprehensive insights and resources, DayTradingBusiness is here to support your trading journey.
Learn about Day Trading Options: What You Need to Know