Did you know that the only thing more volatile than the stock market is your morning coffee? When diving into the world of day trading, understanding the costs involved is crucial for success. This article breaks down the typical expenses associated with day trading, including commissions, platform fees, and the capital required to get started. We’ll explore hidden costs, the impact of taxes and spreads, and how margin and regulatory fees can affect your bottom line. Additionally, we’ll touch on the importance of education, risk management, and the influence of market conditions on your trading expenses. By arming yourself with this knowledge from DayTradingBusiness, you’ll be better prepared to navigate the financial waters of day trading.
What are the typical costs associated with day trading?
Typical costs associated with day trading include:
1. Commissions and Fees: Brokerage commissions per trade, which can range from $0 to several dollars per trade, depending on the broker.
2. Spread Costs: The difference between the bid and ask price, which can add to costs, especially in less liquid markets.
3. Margin Interest: If trading on margin, interest fees for borrowed funds can accumulate quickly.
4. Data and Tools: Subscription fees for real-time data feeds, trading platforms, and analytical tools.
5. Taxes: Short-term capital gains taxes apply to profits from trades held for less than a year.
6. Trading Costs: Costs related to software, hardware upgrades, or high-speed internet connections.
7. Opportunity Costs: Potential losses from missed trades or the time spent on trading instead of other income-generating activities.
Understanding these costs is essential for effective day trading.
How do commissions impact day trading expenses?
Commissions directly increase day trading expenses by reducing overall profits from trades. Each transaction incurs a fee, which can quickly add up, especially with frequent buying and selling. Lower commissions, such as those offered by discount brokers, can help minimize these costs. However, high commission rates can significantly erode returns, making it essential for day traders to factor these fees into their strategies.
What are the fees for using a trading platform?
The fees for using a trading platform typically include commissions on trades, which can range from $0 to $10 per trade, depending on the platform. There may also be spreads, which are the differences between buying and selling prices. Some platforms charge monthly subscription fees or inactivity fees, while others may have account maintenance fees. Additionally, there can be fees for data feeds, margin trading, and withdrawal requests. Always check the specific platform for detailed fee structures.
How much capital do you need to start day trading?
To start day trading, you typically need a minimum of $25,000 in your brokerage account to meet the Pattern Day Trader (PDT) rule. However, you can start with less—around $2,000—but this limits your trading frequency and potential gains. Besides the initial capital, consider costs like commissions, fees, and tools for analysis, which can total $500 to $2,000 monthly, depending on your trading style.
What are the hidden costs of day trading?
The hidden costs of day trading include commissions and fees, which can add up quickly with frequent trades. Slippage occurs when you buy or sell at a different price than expected, affecting profits. Taxes on short-term capital gains can significantly reduce your earnings. Additionally, the emotional toll of constant trading can lead to poor decision-making, resulting in financial losses. Finally, the opportunity cost of time spent trading could mean missed chances in other investments.
How do taxes affect day trading profits?
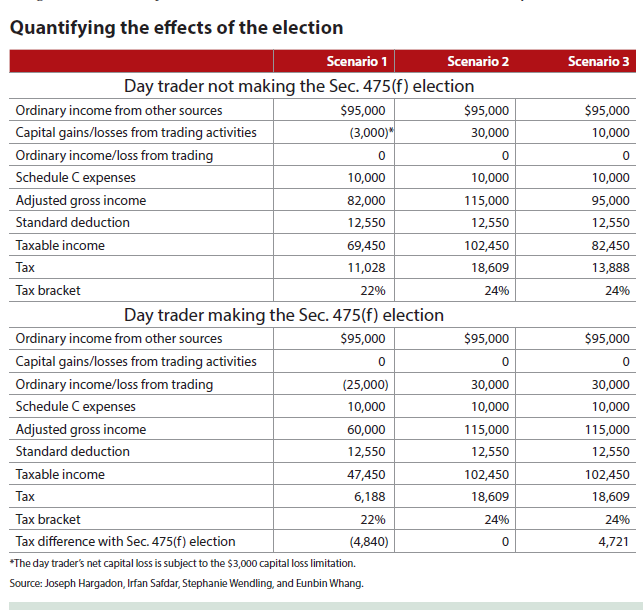
Taxes significantly reduce day trading profits. In the U.S., short-term capital gains from day trading are taxed as ordinary income, which can be as high as 37%. This means that a substantial portion of your earnings goes to taxes, depending on your income bracket. Additionally, trading expenses like commissions and fees can further cut into profits. To maximize gains, it's essential to factor in these tax implications when calculating your overall profitability in day trading.
What are the costs of day trading software?
Day trading software costs vary widely. Basic platforms can range from $0 to $100 per month, while advanced tools with more features may cost between $100 and $500 monthly. Some brokers offer free software with trading commissions. Additionally, consider fees for data feeds, charting tools, and other add-ons, which can add another $50 to $300 monthly. Overall, expect to budget anywhere from $0 to $1,000 monthly depending on your needs and the software's complexity.
How do spreads influence day trading costs?
Spreads directly impact day trading costs by determining the difference between the buying (ask) and selling (bid) prices of a security. A wider spread increases the cost per trade since you need the price to move further in your favor to break even. For active day traders, tighter spreads mean lower transaction costs, enabling more profitable trades. High-frequency trading strategies are particularly sensitive to spreads, as even small differences can significantly affect overall profitability.
What is the impact of margin costs on day trading?
Margin costs significantly affect day trading by amplifying both potential gains and losses. When traders use margin, they borrow funds to increase their buying power. This can lead to higher profits if trades succeed, but also increases the risk of substantial losses if trades go against them. Additionally, margin interest fees can eat into profits, making it crucial for traders to factor these costs into their strategies. Effective risk management becomes essential to mitigate the impact of margin costs on overall profitability.
Are there any regulatory fees for day trading?

Yes, day trading can incur regulatory fees. These may include the SEC fees on sales, FINRA fees for transactions, and potential exchange fees. Additionally, brokers may charge commissions or specific day trading fees. Always check with your broker for detailed costs associated with your trading activity.
How do transaction costs vary between brokers?
Transaction costs vary between brokers based on several factors: commission fees, spreads, and service charges. Some brokers charge a flat fee per trade, while others use a percentage of the trade value. Spreads can differ too; tighter spreads mean lower costs. Additionally, brokers may have different fees for specific services like margin trading or access to advanced trading tools. It's crucial to compare these costs to find a broker that aligns with your day trading strategy.
What Are the Costs and Risks of Day Trading?
Day trading costs include commissions, spreads, and fees for trading platforms. Additionally, there may be costs for market data subscriptions and potential tax implications on short-term capital gains. Consider also the opportunity cost of capital tied up in trades.
Learn more about: What is Day Trading?
What are the costs of day trading education and resources?
Day trading education can cost anywhere from $100 to $10,000 or more, depending on the type of resources. Books and online courses typically range from $50 to $500. Mentorship programs and webinars can run from $500 to $5,000. Brokerage fees and trading platform subscriptions may add $10 to $100 monthly. Additionally, consider the potential losses from trading itself as part of the overall cost.
How can slippage increase day trading expenses?
Slippage increases day trading expenses by causing you to buy at a higher price or sell at a lower price than expected. This difference can erode profits or amplify losses. For example, if you place a market order for a stock at $100, but it executes at $101 due to slippage, you've effectively lost $1 per share. Frequent trading can multiply this effect, significantly impacting overall costs.
What are the costs of risk management in day trading?

The costs of risk management in day trading include commissions and fees for trades, which can add up quickly with frequent transactions. There's also the cost of tools and software for analysis and monitoring, which can range from monthly subscriptions to one-time purchases. Additionally, you may incur costs from educational resources or courses to improve your risk management skills. Finally, consider the potential opportunity cost of capital tied up in trades that don't perform as expected.
How do market conditions affect day trading costs?
Market conditions significantly impact day trading costs by influencing spreads, commissions, and slippage. In volatile markets, spreads widen, increasing costs per trade. High volatility can also lead to greater slippage, where the execution price differs from the expected price, raising overall expenses. During low-volume periods, commissions may increase as traders face higher spreads and less favorable execution. Additionally, market conditions can affect broker fees, such as margin requirements, which can change based on risk assessments. Overall, traders must remain aware of how these conditions can escalate their trading costs.
Learn about How to Find the Right Market for Day Trading
What should I budget for ongoing day trading expenses?
For ongoing day trading expenses, budget for the following key costs:
1. Commissions and Fees: Expect to pay brokerage commissions, which can range from $0 to $10 per trade, depending on the brokerage.
2. Market Data Fees: Professional market data subscriptions can cost $10 to $100 monthly, depending on the level of data you need.
3. Software and Tools: Trading platforms and charting software can range from free to $300+ per month.
4. Internet and Technology: Allocate funds for a reliable internet connection and computer upgrades, totaling about $50 to $150 monthly.
5. Education and Training: Consider ongoing education costs, which can vary widely, from free resources to courses costing $500 or more.
6. Taxes: Don’t forget about capital gains taxes, which can significantly impact your profits.
Overall, a monthly budget of $200 to $600 is common, but it can vary based on your trading volume and chosen tools.
Conclusion about What are the Costs of Day Trading?
In summary, understanding the costs of day trading is crucial for effective financial planning and risk management. From commissions and platform fees to hidden costs like slippage and taxes, each expense can significantly impact your overall profitability. Proper budgeting, including ongoing expenses and education costs, is essential to navigate the day trading landscape successfully. By being aware of these factors, traders can make informed decisions and optimize their strategies. For more comprehensive insights and guidance, consider exploring the resources offered by DayTradingBusiness.