Did you know that more than $6 trillion is traded in the Forex market every day, which is enough to buy a small island? Understanding the differences between Forex and other day trading markets is essential for any trader looking to maximize their potential. This article dives into key distinctions, such as how Forex trading compares to stocks and futures, its unique advantages, specific risks, and the impact of leverage. Additionally, we’ll explore trading hours, liquidity, market volatility, common strategies, transaction costs, and the regulatory environment. Join us as we unravel what makes Forex a standout choice in the world of day trading, brought to you by DayTradingBusiness.
What are the key differences between Forex and stock trading?
The key differences between Forex and stock trading include:
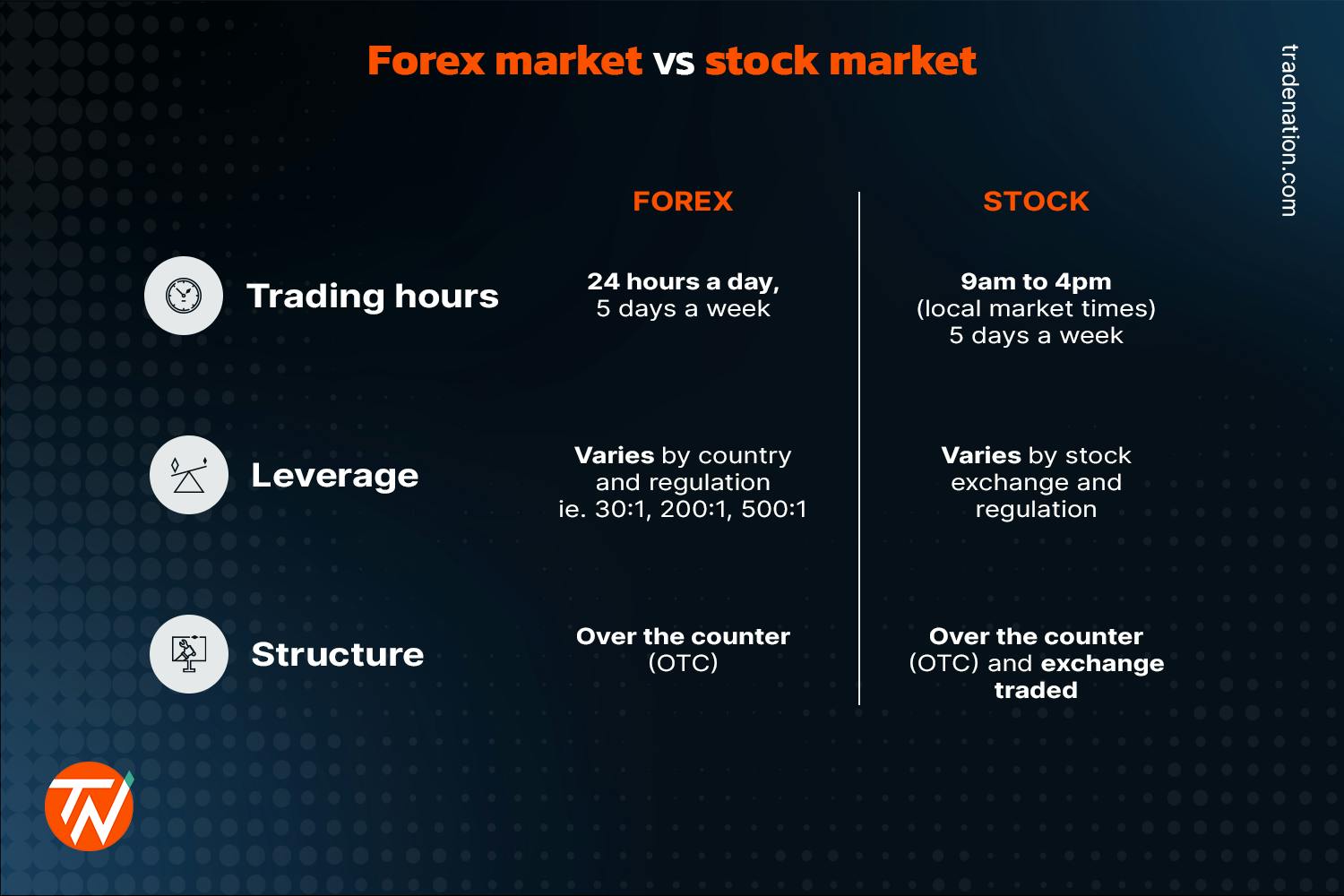
1. Market Hours: Forex operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, while stock markets have specific trading hours.
2. Liquidity: Forex has higher liquidity due to the vast volume of trades, making it easier to enter and exit positions quickly compared to stocks.
3. Leverage: Forex typically offers greater leverage, allowing traders to control larger positions with less capital, unlike stocks which usually have lower leverage limits.
4. Asset Classes: Forex involves trading currency pairs, whereas stock trading focuses on individual company shares.
5. Volatility: Forex can experience rapid price fluctuations due to geopolitical events and economic data releases, while stock prices may be influenced by company-specific news.
6. Costs: Forex trading often has lower transaction costs and spreads compared to stock trading, which can involve commissions and fees.
7. Market Influencers: Forex is influenced by macroeconomic factors, while stock prices are more affected by company performance and earnings reports.
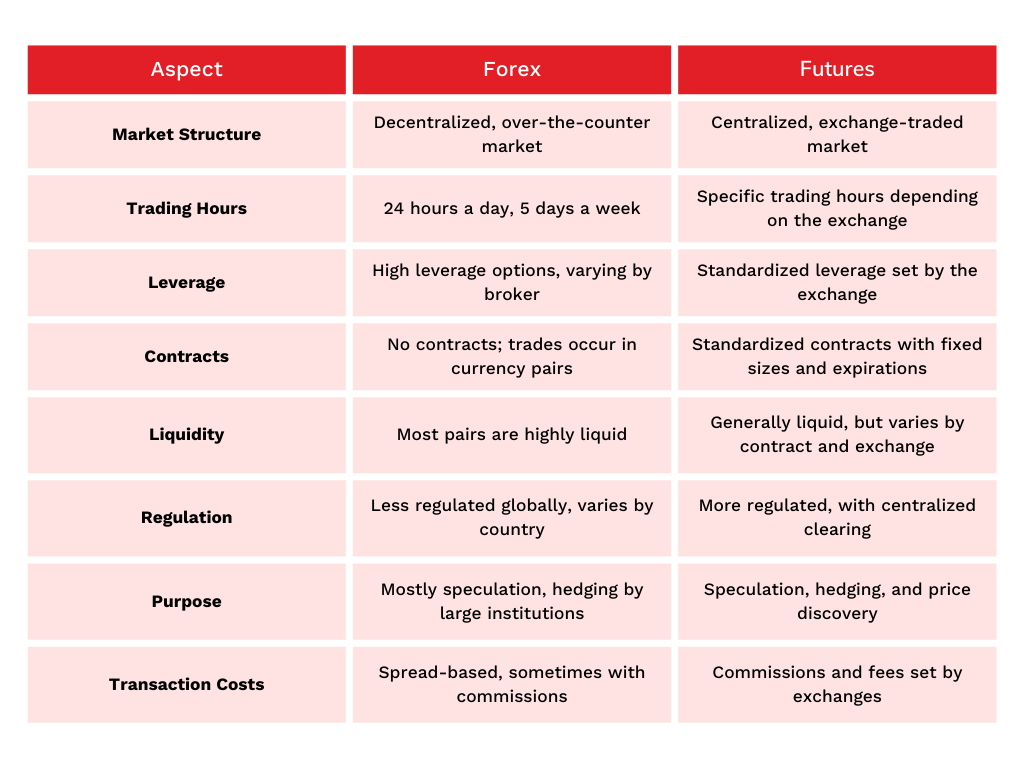
How does Forex trading compare to futures trading?
Forex trading involves buying and selling currency pairs, focusing on exchange rate fluctuations, while futures trading involves contracts to buy or sell commodities or financial instruments at a predetermined price in the future. Forex typically has higher liquidity, operates 24 hours a day, and requires less capital to start. Futures trading is often more regulated, can involve leverage, and is linked to specific expiration dates. Overall, Forex is more accessible and flexible, while futures provide structured trading with defined contracts.
What makes Forex unique among day trading markets?
Forex is unique among day trading markets due to its high liquidity, 24-hour trading availability, and low transaction costs. Unlike stock markets, Forex operates globally across different time zones, allowing traders to enter and exit positions at any time. The diverse range of currency pairs offers various trading opportunities. Additionally, leverage in Forex can be significantly higher than in other markets, amplifying potential gains—and losses. Lastly, Forex is less influenced by individual company performance, making it more dependent on macroeconomic factors and geopolitical events.
What are the advantages of trading Forex over other markets?
Forex trading offers several advantages over other markets. Firstly, it has high liquidity, allowing for quicker transactions and tighter spreads. Secondly, the Forex market operates 24 hours a day, enabling traders to react to global news anytime. Thirdly, leverage is commonly available, allowing for larger positions with a smaller initial investment. Additionally, there are lower transaction costs compared to stocks or futures, making it more accessible for retail traders. Finally, Forex trading offers a wide variety of currency pairs, providing diverse trading opportunities.
Are there specific risks associated with Forex trading?

Yes, Forex trading carries specific risks, including high volatility, leverage risk, and market manipulation. Unlike stocks, Forex markets can swing dramatically due to economic news or geopolitical events. Leverage can amplify gains but also leads to significant losses. Additionally, the 24-hour nature of Forex trading means traders may face unexpected price movements during off-hours. Understanding these risks is crucial for effective Forex trading compared to other day trading markets like stocks or commodities.
How does leverage in Forex differ from stock trading?
Leverage in Forex typically ranges from 50:1 to 500:1, allowing traders to control large positions with a small amount of capital. In stock trading, leverage is usually lower, often capped at 2:1 or 4:1. This means Forex traders can amplify their potential profits (and losses) significantly more than stock traders. Additionally, Forex markets are more volatile, which increases the risk associated with high leverage. In summary, Forex offers higher leverage and greater risk compared to stock trading.
What are the trading hours for Forex compared to other markets?
Forex trading hours are 24 hours a day, five days a week, starting from Sunday evening to Friday evening. This continuous operation allows for trading in different global markets, such as Sydney, Tokyo, London, and New York. In contrast, stock markets typically operate during specific hours, usually around 9:30 AM to 4 PM local time, with some pre-market and after-hours trading available. Futures markets also have set hours, often mirroring stock market schedules, but with some extended trading sessions. This flexibility makes Forex unique compared to the more limited trading hours of other markets.
What are the key differences between Forex day trading and other day trading markets?
The main differences between Forex and other day trading markets are liquidity, trading hours, and leverage. Forex markets offer higher liquidity due to their size, allowing for easier entry and exit. They operate 24 hours a day, unlike stock markets that have specific trading hours. Additionally, Forex trading typically provides higher leverage, enabling traders to control larger positions with less capital compared to other markets.
Learn more about: Understanding Forex Day Trading Markets
How does liquidity in Forex differ from futures or stock markets?
Liquidity in Forex is typically higher than in futures or stock markets. This is due to the 24-hour trading cycle and the vast volume of transactions, allowing for quick entry and exit from trades. In Forex, major currency pairs have tight spreads and minimal slippage. In contrast, futures markets can be less liquid, especially for less popular contracts, leading to wider spreads. Stock markets vary; large-cap stocks may have high liquidity, while small-cap stocks can be more illiquid. Overall, Forex offers the highest liquidity, enhancing trading efficiency.
What factors influence Forex prices versus stock prices?
Forex prices are influenced by factors like interest rates, economic indicators, geopolitical events, and market sentiment. In contrast, stock prices are driven by company performance, earnings reports, market trends, and sector health. Currency fluctuations often respond to macroeconomic data, while stocks react to microeconomic factors specific to individual companies. Additionally, Forex markets operate 24/5, leading to instant reactions to global news, whereas stock markets have set trading hours.
How does market volatility in Forex compare to other trading markets?
Forex market volatility is generally higher than in stock or commodity markets due to its 24-hour nature and massive liquidity. Currency pairs react quickly to economic news and geopolitical events, leading to rapid price swings. In contrast, stock markets have set trading hours and can be influenced by company-specific factors, resulting in less frequent volatility spikes. Overall, Forex presents more opportunities for quick trades but also higher risks compared to other trading markets.
What are the common strategies used in Forex versus other day trading?
Common strategies in Forex include scalping, trend following, and range trading. Scalping focuses on small price changes, often executing multiple trades within a day. Trend following aims to capitalize on the direction of currency movements, while range trading exploits price oscillations between support and resistance levels.
In contrast, day trading in stocks often uses strategies like momentum trading, news-based trading, and breakout trading. Momentum trading looks for stocks gaining traction, news-based trading reacts to earnings reports or announcements, and breakout trading identifies price movements beyond established levels.
Overall, Forex strategies emphasize currency pairs and global economic indicators, while stock day trading often relies on company-specific news and market sentiment.
How do transaction costs in Forex differ from other trading platforms?
Transaction costs in Forex typically include spreads and commissions, which are often lower than those in stock or options trading. Forex spreads can be as tight as 0.1 pips for major currency pairs, while stock commissions can range from $5 to $10 per trade. Additionally, Forex operates 24/5, allowing for continuous trading without additional fees for after-hours trading, unlike many stock platforms. Overall, Forex can offer more cost-effective trading options due to these lower transaction costs and reduced fees.
What types of analysis are best for Forex compared to stocks?
For Forex, technical analysis is often preferred due to the market's high liquidity and volatility. Traders use chart patterns, indicators, and price action analysis to identify trends and entry points. Fundamental analysis is also important, focusing on economic indicators, interest rates, and geopolitical events that impact currency values.
In contrast, stock trading typically relies more on fundamental analysis, evaluating company performance, earnings reports, and market conditions. While technical analysis is still used in stocks, the emphasis on company financials sets it apart from Forex.
In summary, Forex benefits from a blend of technical and fundamental analysis, while stocks lean more heavily on fundamental analysis.
How does the regulatory environment for Forex differ from other markets?
The regulatory environment for Forex differs from other markets mainly in the level of oversight and the entities involved. Forex is often less regulated than stock markets, with different countries having varying rules. In the U.S., Forex trading is regulated by the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the National Futures Association (NFA), which impose strict guidelines on leverage and broker practices. In contrast, stock markets are typically overseen by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), which has more stringent requirements regarding disclosure and transparency.
Additionally, Forex brokers can operate with less capital than stock brokers, leading to a wider range of broker quality and practices. This creates a need for traders to conduct thorough research when choosing a Forex broker, unlike more standardized stock trading environments. Overall, Forex’s regulatory landscape is more fragmented and less uniform than that of equities and futures markets.
What are the typical trading platforms for Forex versus stock trading?
Typical trading platforms for Forex include MetaTrader 4 (MT4), MetaTrader 5 (MT5), and cTrader. For stock trading, common platforms are TD Ameritrade, E*TRADE, and Charles Schwab. Forex platforms often focus on currency pairs and leverage, while stock platforms provide tools for equity analysis, options trading, and market research.
How do Forex trading pairs differ from stocks or futures contracts?
Forex trading pairs involve the simultaneous buying and selling of currencies, while stocks represent ownership in a company and futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell an asset at a future date. Forex operates 24/5 with high liquidity and leverage, making it distinct from stock and futures markets, which have set trading hours and different levels of volatility. Additionally, Forex trading pairs are quoted in terms of one currency against another, while stocks are priced individually and futures are based on underlying assets like commodities or indices.
Conclusion about Differences Between Forex and Other Day Trading Markets
In summary, understanding the differences between Forex and other day trading markets is crucial for making informed trading decisions. Forex offers unique advantages such as high liquidity, flexible trading hours, and significant leverage, but it also comes with specific risks. By grasping how Forex trading compares to stocks and futures, traders can better navigate market volatility, transaction costs, and regulatory environments. For those seeking deeper insights and strategies tailored to the Forex landscape, DayTradingBusiness provides valuable resources and support to enhance your trading journey.
Learn about Differences Between Crypto Day Trading and Other Markets