Did you know that nearly 90% of day traders lose money? But don't worry—understanding the fundamentals can turn the tide in your favor! In this article, we dive into the essential differences between long and short options trading strategies, helping you grasp how each method works in day trading. We’ll explore the benefits and risks associated with these strategies, discuss market volatility's impact, and provide insights into effective trading plans. Additionally, you’ll learn how to leverage technical analysis and consider tax implications to enhance your trading decisions. With insights from DayTradingBusiness, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the dynamic world of options trading.
What are the key differences between long and short options trading strategies?
Long options trading strategies involve buying options contracts, expecting the underlying asset's price to move significantly in a favorable direction. This strategy offers unlimited profit potential with a limited loss, defined by the premium paid for the option.
Short options trading strategies involve selling options contracts, expecting the underlying asset's price to either stay the same or move against the option buyer. This approach provides limited profit potential (the premium received) and carries higher risk, as losses can be substantial if the market moves unfavorably.
In summary, long options focus on potential gains with limited risk, while short options emphasize income generation with higher risk exposure.
How do long options strategies work in day trading?
Long options strategies in day trading involve buying call or put options to benefit from price movements. When you buy a call option, you expect the underlying asset to rise; when you buy a put option, you anticipate a decline.
In a long call strategy, if the stock price exceeds the strike price before expiration, you can sell the option for a profit. In a long put strategy, if the stock drops below the strike price, you can also sell for a profit.
The key is to choose the right strike price and expiration date, as these factors impact potential gains and losses. Day traders often look for quick movements to capitalize on volatility, aiming for high reward-to-risk ratios.
Overall, long options allow traders to leverage their capital while limiting losses to the premium paid for the options.
What are the benefits of using short options strategies?
Short options strategies can offer several benefits in day trading. They provide income generation through premium collection, allowing traders to profit from time decay. These strategies can also limit risk exposure compared to holding long options, as they typically involve less capital. Additionally, short options can enhance flexibility, enabling traders to adjust positions quickly based on market movements. Lastly, they can serve as effective hedges against long positions, reducing potential losses in volatile markets.
When should I use long options versus short options?
Use long options when you expect significant price movement in the underlying asset and want to leverage that with limited risk. Opt for long calls if you anticipate a price increase, and long puts if you expect a decline.
Choose short options when you believe the underlying asset will not move much, allowing you to collect premiums. Short calls are ideal in a bearish or neutral market, while short puts work well if you expect slight bullish movement.
In summary, go long for potential gains with higher volatility and short for income in stable markets.
What risks are associated with long options trading?
Long options trading involves several risks. First, the primary risk is losing the entire premium paid if the option expires worthless. Second, volatility can impact option prices, leading to potential losses even if the underlying asset moves in the desired direction. Third, time decay erodes the value of options as expiration approaches, which can diminish profits. Lastly, market conditions can change rapidly, resulting in unexpected losses.
How can I minimize risks when trading short options?
To minimize risks when trading short options, consider these strategies:
1. Use Stop Loss Orders: Set stop loss orders to limit potential losses on your trades.
2. Choose Liquid Options: Trade highly liquid options to ensure tighter spreads and easier executions.
3. Sell Options with High Implied Volatility: Sell options when implied volatility is high, as they are more likely to decrease in value.
4. Diversify Your Positions: Avoid concentrating on one stock or sector to reduce overall risk.
5. Use Spreads: Implement strategies like vertical spreads to cap potential losses while still allowing for profit.
6. Manage Position Size: Limit the size of each trade to a small percentage of your portfolio.
7. Monitor Market Conditions: Stay updated on market news and trends that could affect your options.
8. Educate Yourself: Continuously learn about options trading strategies and risk management techniques.
By following these practices, you can effectively manage and minimize risks associated with trading short options.
What are common long options strategies for day traders?
Common long options strategies for day traders include:
1. Long Call: Buying call options to profit from an expected increase in the underlying asset's price.
2. Long Put: Purchasing put options to capitalize on an anticipated decline in the underlying asset's price.
3. Vertical Spread: Buying a call or put at one strike price while selling another at a different strike price to limit risk and reduce costs.
4. Straddle: Buying both a call and a put at the same strike price, betting on high volatility in either direction.
5. Strangle: Similar to a straddle but with different strike prices, offering a cheaper way to profit from large price movements.
These strategies help day traders manage risk while aiming for quick profits.
What are effective short options strategies for maximizing profits?
Effective short options strategies for maximizing profits include:
1. Naked Call Selling: Sell call options without owning the underlying stock, profiting from time decay and volatility drops if the stock remains below the strike price.
2. Cash-Secured Puts: Sell put options while holding enough cash to buy the stock if assigned, allowing you to collect premium and potentially acquire shares at a lower price.
3. Iron Condor: Combine selling out-of-the-money puts and calls, profiting from low volatility as long as the stock stays within the range defined by the strike prices.
4. Vertical Spreads: Implement bear call spreads or bull put spreads, capping potential losses while profiting from directional moves in the stock.
5. Straddles and Strangles: Use these strategies to profit from significant price movements, benefiting from volatility whether the stock moves up or down.
These strategies can enhance profit potential while managing risk in day trading options.
How does market volatility affect long vs. short options?
Market volatility impacts long and short options differently.
For long options, increased volatility can enhance potential profits. Higher volatility raises the option's premium, allowing traders to sell for more if the underlying asset moves favorably.
In contrast, short options suffer from volatility. When volatility spikes, the risk of loss increases as the underlying asset can move significantly against the position. This can lead to larger potential losses than anticipated.
In summary, long options benefit from volatility, while short options face heightened risk.
What indicators should I consider for long options trading?
For long options trading, consider these key indicators:
1. Implied Volatility: Look for low implied volatility; this suggests options are cheaper and potential for profit increases if volatility rises.
2. Delta: Choose options with a higher delta to increase responsiveness to price movements of the underlying asset.
3. Open Interest: Higher open interest indicates more liquidity, which is crucial for entering and exiting positions easily.
4. Support and Resistance Levels: Identify strong support levels for buying calls and resistance for puts to gauge potential price movements.
5. Momentum Indicators: Use tools like RSI or MACD to identify bullish trends. Look for bullish signals before entering long positions.
6. Earnings Reports: Be aware of upcoming earnings announcements, as they can significantly impact stock prices and volatility.
7. Market Sentiment: Gauge overall market sentiment through news, social media, and analyst reports to align your trades with broader trends.
These indicators can help you make informed decisions in long options trading.
How do long and short strategies in options trading compare for day trading?
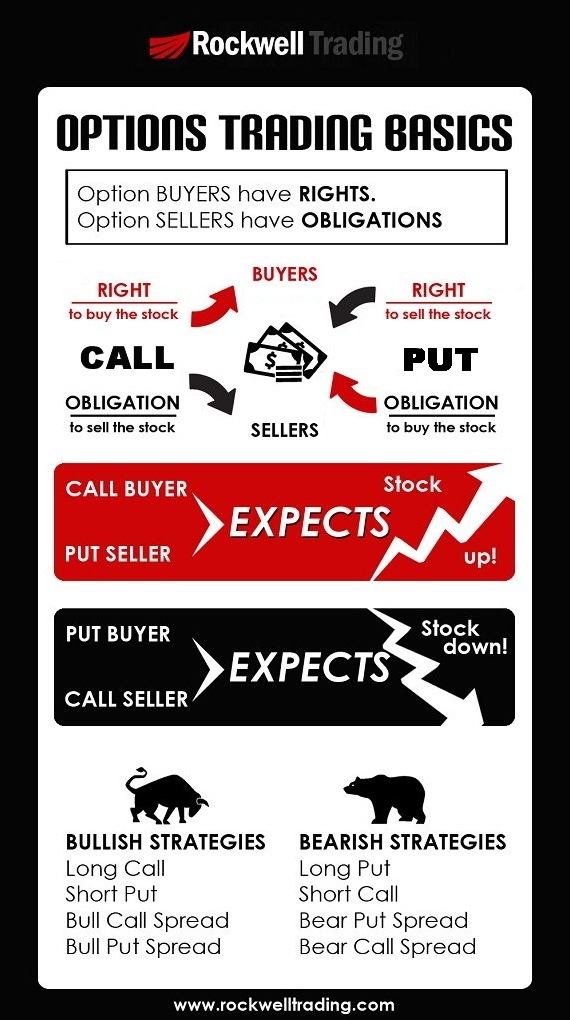
In day trading options, long strategies involve buying options to profit from price increases, while short strategies involve selling options to profit from price decreases. Long strategies include buying calls or puts, whereas short strategies can involve writing calls or puts.
Learn more about: Understanding Options in Day Trading
Learn about How to Backtest Futures Day Trading Strategies
What indicators are important for short options trading?
Key indicators for short options trading include:
1. Implied Volatility (IV): High IV suggests overpricing of options, making it a good time to sell.
2. Open Interest: Look for options with high open interest to ensure liquidity.
3. Delta: A lower delta indicates less sensitivity to price changes, making it favorable for short positions.
4. Volume: High trading volume signals strong interest and can indicate potential price movement.
5. Support and Resistance Levels: Identify key levels to gauge potential price reversals.
6. Time Decay (Theta): Understand how quickly options lose value as expiration approaches—beneficial for short sellers.
Use these indicators to enhance your short options trading strategies effectively.
How do time decay and expiration impact long and short options?
Time decay negatively impacts long options because their value decreases as expiration approaches, making it harder to profit. For short options, time decay works in your favor; the option’s value decreases, increasing your potential profit if the option expires worthless. Expiration is critical for both strategies: long options need significant price movement before expiration to be profitable, while short options can capitalize on stagnant or declining prices as they near expiration.
What are the tax implications of day trading options?
Day trading options can have significant tax implications. Profits from day trading are typically considered short-term capital gains, taxed at your ordinary income tax rate. If you hold options for less than a year before selling, you’ll pay these higher rates. Additionally, frequent trading may classify you as a "trader," allowing you to deduct trading-related expenses, but you'll need to meet specific IRS criteria. Remember, losses can offset gains, and you can carry them forward to future years. Always consult a tax professional for personalized advice.
Learn about Tax Implications of Forex Day Trading
How can I develop a long options trading plan?

To develop a long options trading plan, follow these steps:
1. Define Goals: Set clear profit targets and risk tolerance.
2. Choose Strategies: Focus on strategies like buying calls or puts for bullish or bearish views, respectively.
3. Market Analysis: Conduct technical and fundamental analysis to identify potential stocks or indices to trade.
4. Select Expiration Dates: Pick expiration dates that align with your market outlook—consider shorter for quick trades, longer for more time to realize gains.
5. Determine Entry and Exit Points: Establish criteria for entering trades and set profit and stop-loss levels.
6. Risk Management: Use position sizing to limit losses and diversify your trades to manage risk.
7. Track Performance: Keep a trading journal to analyze your trades and refine your plan based on results.
Implement these components to create an effective long options trading plan.
What should I include in a short options trading strategy?
Include the following in a short options trading strategy:
1. Market Analysis: Use technical analysis to identify trends and potential entry and exit points.
2. Strategy Type: Decide between long strategies (buying calls or puts) for bullish or bearish outlooks, or short strategies (selling calls or puts) if you expect stagnation or a decline.
3. Risk Management: Set stop-loss orders and define how much capital you’re willing to risk on each trade.
4. Position Sizing: Determine the size of your trades based on your total capital and risk tolerance.
5. Time Frame: Specify whether you’re day trading or holding positions for a few days, aligning your strategy with your chosen time frame.
6. Exit Strategy: Plan how and when you’ll exit trades, whether for profit-taking or cutting losses.
7. Review and Adjust: Regularly evaluate your trades and adjust your strategy based on performance and market conditions.
How can I use technical analysis for long and short options trading?
To use technical analysis for long and short options trading, follow these steps:
1. Identify Trends: Use charts to spot upward or downward trends. Look for patterns like head and shoulders or double tops to forecast price movements.
2. Use Indicators: Apply indicators like moving averages, RSI, or MACD to gauge momentum and potential reversals. For long options, seek bullish signals; for short options, look for bearish signals.
3. Support and Resistance: Determine key support and resistance levels. Buy call options (long) near support and sell call options (short) near resistance.
4. Volume Analysis: Monitor trading volume to confirm trends. Increasing volume on price movements strengthens the signal for your options strategy.
5. Time Frame Consideration: Choose appropriate time frames for your trades. Day trading often requires shorter time frames, like 5-minute or 15-minute charts.
6. Risk Management: Set stop-loss orders based on technical levels to limit losses. For long options, consider a stop-loss below a recent low; for short options, above a recent high.
7. Market Sentiment: Keep an eye on news and events that could impact volatility. Use implied volatility metrics to gauge market sentiment and adjust strategies accordingly.
Apply these techniques to refine your long and short options trading strategies effectively.
Learn about How to Use Technical Analysis for Options Day Trading
Conclusion about Day Trading Options: Long vs. Short Strategies
In summary, understanding the nuances between long and short options trading strategies is crucial for effective day trading. Long options provide opportunities for growth, while short options can yield quick profits in declining markets. Each strategy has its own set of risks and benefits, making it essential to assess market conditions and personal risk tolerance. By leveraging key indicators and developing structured trading plans, traders can optimize their approaches and enhance profitability. For comprehensive insights and guidance on navigating these strategies, DayTradingBusiness is here to support your trading journey.
Learn about Day Trading Options: Strategies for Different Markets