Did you know that options trading can sometimes feel like playing poker with a deck of cards that keeps changing? In the fast-paced world of day trading, understanding options pricing is crucial for success. This article breaks down the essentials, covering the intrinsic and extrinsic values that shape options prices, the impact of time decay, and the role of implied volatility. You'll learn how news events, supply and demand dynamics, and market conditions influence pricing trends. We’ll also explore key pricing models like Black-Scholes, the differences between call and put options, and the importance of the Greeks in your trading strategy. Plus, we’ll highlight common mistakes to avoid and how to calculate your break-even point. Join DayTradingBusiness as we navigate these critical concepts to enhance your trading skills.
What is options pricing in day trading?
Options pricing in day trading refers to the valuation of options contracts based on various factors like the underlying asset's price, strike price, time until expiration, volatility, and interest rates. The most common model used is the Black-Scholes model, which calculates the theoretical price of options. Traders analyze these prices to make informed decisions about buying or selling options, aiming to profit from short-term price movements. Understanding implied volatility is crucial, as it indicates market expectations for future price fluctuations.
How do intrinsic and extrinsic value affect options pricing?
Intrinsic value is the difference between the current price of the underlying asset and the strike price of the option. If an option is in-the-money, it has intrinsic value; if it's out-of-the-money, it has none. Extrinsic value, or time value, reflects the potential for the option to gain value before expiration, influenced by factors like time remaining and volatility.
In options pricing, the total price (premium) equals intrinsic value plus extrinsic value. When the underlying asset approaches the strike price, intrinsic value increases, often raising the option's premium. Conversely, as expiration nears, extrinsic value diminishes, a phenomenon known as time decay, impacting the pricing of options in day trading. Understanding these components helps traders make informed decisions.
What factors influence options pricing in day trading?
Options pricing in day trading is influenced by several key factors:
1. Underlying Asset Price: The current price of the underlying asset directly affects the option's intrinsic value.
2. Strike Price: The difference between the option's strike price and the underlying asset's price determines its potential profitability.
3. Time to Expiration: Options lose value as they approach expiration, a phenomenon known as time decay.
4. Volatility: Higher volatility increases the option's premium due to greater uncertainty about future price movements.
5. Interest Rates: Changes in interest rates can impact the cost of carry and, subsequently, option pricing.
6. Dividends: Expected dividends from the underlying asset can influence option pricing, especially for calls.
These factors interplay to determine the market price of options, crucial for day traders making quick decisions.
How does time decay impact options pricing?
Time decay decreases the value of options as they approach expiration. This effect, known as theta, means that the premium of options erodes over time, especially for out-of-the-money options. As expiration nears, the rate of decay accelerates, making options less valuable if they aren’t in-the-money. Day traders need to monitor time decay closely to make informed decisions on buying or selling options, as it directly affects potential profit and loss.
What is implied volatility and its role in options pricing?
Implied volatility (IV) represents the market's forecast of a stock's price fluctuations and is a key factor in options pricing. Higher IV indicates that traders expect significant price swings, leading to higher option premiums. Conversely, lower IV suggests less expected movement, resulting in cheaper options. In day trading, understanding IV helps traders assess potential profitability and risk, guiding their buying and selling decisions. It’s crucial for determining whether options are overpriced or underpriced in the current market context.
How can news events affect options pricing?
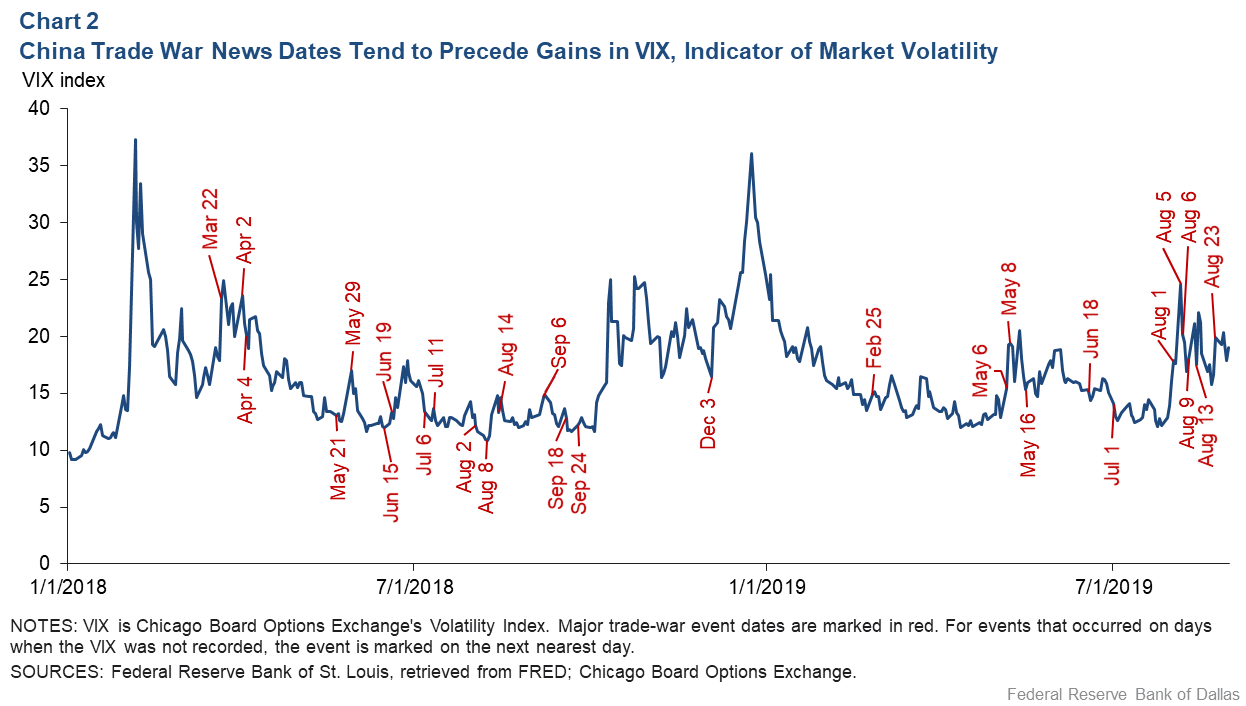
News events can significantly impact options pricing by causing volatility and altering market expectations. Positive news can increase a stock's price, leading to higher call option premiums. Conversely, negative news can drive prices down, raising put option values. Implied volatility often spikes around major announcements, affecting the pricing of options. Traders anticipate these shifts, adjusting their strategies based on expected market reactions to the news.
What are the key models for options pricing?
The key models for options pricing are:
1. Black-Scholes Model: This widely used model calculates the theoretical price of European options based on factors like stock price, strike price, time to expiration, risk-free interest rate, and volatility.
2. Binomial Model: This model uses a discrete-time framework to evaluate options. It builds a price tree to assess possible future stock prices and the corresponding option values at each node.
3. Monte Carlo Simulation: This statistical method simulates a range of possible price paths for the underlying asset to estimate the option’s value, often used for complex options.
4. Garman-Kohlhagen Model: Specifically for foreign exchange options, it accounts for the interest rate differential between currencies.
5. Heston Model: This model incorporates stochastic volatility, allowing for a more dynamic assessment of option pricing compared to static models.
These models help traders make informed decisions in day trading by providing a structured way to evaluate options.
How Do Options Pricing Strategies Affect Day Trading Success?
Understanding options pricing in day trading involves evaluating factors like intrinsic value, time decay, and implied volatility. Intrinsic value is the difference between the underlying asset's current price and the option's strike price. Time decay refers to the reduction in an option's value as it approaches expiration. Implied volatility reflects market expectations of future price fluctuations, impacting the option's premium.
Learn more about: Understanding Options in Day Trading
How do supply and demand dynamics influence options pricing?
Supply and demand dynamics directly impact options pricing by affecting the premium. When demand for an option increases, prices rise due to competition among traders. Conversely, if supply outstrips demand, prices drop.
Market sentiment, news, and underlying asset volatility also play crucial roles. For example, if traders expect significant movement in a stock, demand for its options may surge, driving up prices. Conversely, if a stock is stable, less interest leads to lower option premiums.
In day trading, quick shifts in supply and demand can create opportunities for profit, making it essential to monitor these dynamics closely.
What is the Black-Scholes model for options pricing?
The Black-Scholes model is a mathematical formula used to calculate the theoretical price of European-style options. It considers factors like the current stock price, the option's strike price, time until expiration, risk-free interest rate, and the stock's volatility. The model helps traders determine whether an option is fairly priced, overvalued, or undervalued, aiding in day trading decisions.
How do dividends impact options pricing?
Dividends impact options pricing primarily by influencing the underlying stock's expected future price. When a stock pays a dividend, the stock price typically drops on the ex-dividend date by the dividend amount. This affects call and put options differently: call options may decrease in value due to the expected drop in stock price, while put options might increase in value as the stock becomes less attractive. Traders need to adjust their pricing models to account for dividends, as they affect implied volatility and the time value of options.
What are the differences between call and put options pricing?
Call and put options pricing differ based on their intrinsic value and time value.
A call option gives the buyer the right to purchase an asset at a specified price, so its price increases when the underlying asset's price rises. Its pricing reflects the likelihood of the asset exceeding the strike price before expiration.
Conversely, a put option gives the buyer the right to sell an asset at a specified price, making its price rise when the underlying asset's price falls. Its pricing accounts for the probability of the asset dropping below the strike price before expiration.
Both options also factor in time decay, volatility, and interest rates, but in different ways. Call options usually benefit more from increasing volatility, while put options can gain when market conditions suggest a downturn.
How can day traders use options pricing strategies effectively?
Day traders can use options pricing strategies effectively by focusing on key concepts like implied volatility, time decay, and the Greeks.
1. Implied Volatility: Monitor changes in implied volatility to identify potential price movements. High volatility often leads to higher option premiums, which can be advantageous for selling options.
2. Time Decay (Theta): Understand that options lose value as expiration approaches. Day traders can benefit from selling options to capitalize on time decay, especially during low volatility periods.
3. The Greeks: Use Delta to gauge how much an option's price will move relative to the underlying stock. Gamma helps in understanding how Delta changes, while Vega measures sensitivity to volatility changes. These metrics can guide entry and exit points.
4. Spread Strategies: Implement strategies like credit spreads or iron condors to limit risk while maximizing potential profits. These can work well in sideways markets.
5. Market Sentiment: Pay attention to market news and events that can affect options pricing. Timing trades around earnings reports or economic releases can enhance profitability.
By combining these strategies, day traders can make informed decisions and improve their chances of success in options trading.
Learn about How to Use Technical Analysis for Options Day Trading
What is the Greeks' role in understanding options pricing?
The Greeks help traders understand options pricing by quantifying risk and sensitivity to various factors. Delta measures how much an option's price changes with the underlying asset's movement. Gamma shows the rate of change of delta, indicating how sensitive an option is to price fluctuations. Theta represents time decay, revealing how much value an option loses as expiration approaches. Vega assesses the impact of volatility on an option's price. By analyzing these Greeks, traders can make informed decisions about when to buy or sell options based on market conditions.
How do market conditions affect options pricing trends?
Market conditions significantly impact options pricing trends. In volatile markets, options prices usually increase due to higher implied volatility, reflecting greater uncertainty. Conversely, in stable markets, options prices tend to decrease as implied volatility drops. Economic indicators, interest rates, and market sentiment also play crucial roles; strong bullish sentiment can inflate call option prices, while bearish trends may boost put options. Additionally, supply and demand dynamics can shift pricing trends, making it essential for day traders to monitor these conditions closely.
What are common mistakes in interpreting options pricing?
Common mistakes in interpreting options pricing include misunderstanding implied volatility, ignoring time decay, and miscalculating intrinsic versus extrinsic value. Traders often overestimate the impact of implied volatility on prices, leading to poor trade decisions. Many also neglect how time decay erodes options’ value, especially as expiration approaches. Additionally, failing to differentiate between intrinsic value (the actual value of the option) and extrinsic value (the premium above intrinsic value) can result in misguided evaluations. Lastly, not considering market conditions or news events can skew interpretations of options pricing.
How can I calculate the break-even point for options trades?
To calculate the break-even point for options trades, follow these steps:
1. Identify the Premium: Determine the cost of the option (the premium paid).
2. For Call Options: Add the premium to the strike price. Break-even = Strike Price + Premium.
3. For Put Options: Subtract the premium from the strike price. Break-even = Strike Price – Premium.
4. Consider Commissions: Factor in any commission fees that may affect the total cost.
This gives you the price at which your trade becomes profitable.
Conclusion about Understanding Options Pricing in Day Trading
In summary, mastering options pricing is essential for successful day trading. Understanding intrinsic and extrinsic values, the impact of time decay, implied volatility, and market dynamics enables traders to make informed decisions. By leveraging pricing models and strategies, as well as recognizing the influence of news events and market conditions, traders can enhance their profitability. For those looking to deepen their knowledge and navigate the complexities of options trading, DayTradingBusiness offers invaluable insights and resources.
Learn about Frequently Asked Questions About Day Trading Options
Sources:
- Why do option returns change sign from day to night? - ScienceDirect
- Why Option Prices Lag Stock Prices: A Trading-Based Explanation
- The Price of Macroeconomic Uncertainty: Evidence from Daily Options
- The Intuition Behind Option Valuation: A Teaching Note
- Understanding Equity Option Returns in the Chinese Market by ...